Google Apps Email Hosting/Management, The Best of the Best
Comments Off on Google Apps Email Hosting/Management, The Best of the Best
If you have your own domain name, and purchase a shared hosting account for it, you can often create and host e-mail addresses for that domain with the web host. For example, the control panel on your web host (for me this is cPanel) might enable you to: create many addresses@yourdomain.com; check the mail directly on the server; check the mail remotely from a different web client or a desktop program; handle forwarding to other addresses; manage spam blocking; and more.
Why e-mail hosting with your shared hosting provider is sub-optimal
Hosting your e-mail on the same server as your website is often convenient. However, in the typical shared hosting environment, your messages might not always be sent and received in a timely and reliable manner. As good as my shared web host has been for serving web pages, I’d rather not use it for e-mail. Here are a few reasons why:
- Clogged e-mail queues: With potentially hundreds of other people using the same machine as you, you have no idea as to whether one or all of those people (including regular new customers) is going to be a heavy e-mail user, or worse, a spammer. Therefore, with server resources trying to serve pages and unpredictable volumes of mail, it is more likely to get bogged down in a shared environment. I have experienced this many times, where people took hours to receive my mail or I was receiving their mail days after they’d sent it. Often this was due to only one other heavy user on the machine: they were spamming or had a script hacked, thus resulting in backed up e-mail processing queues.
- Blocked IP address: If you have a spammer on your machine, they don’t even need to be a heavy user to cause damage. If someone complains that spam is being sent from your server, external e-mail providers are often quick to temporarily block any mail coming from that server’s IP. This affects you even if your domain was not the problem. In that case, outgoing mail is definitely hindered but you might also have trouble receiving mail if you forward it somewhere else.
- Limited storage space: When you purchase shared hosting, you are often thinking about the space you need for your website. A typical blog with only text and pictures takes years to even use up 100mb of space. If you choose to leave e-mail on your server, you can quickly outgrow your hosting account based on e-mail alone.
Reasons to handle e-mail with Google Apps
Google Apps is a free service that can handle many aspects — most importantly for me is e-mail — associated with your domain. It is not a particularly new service, but I recently made the decision to switch my e-mail handling over to Google; it was painless and definitely worth it. Basically, you get the same e-mail access as with a normal Gmail account, but for addresses for your domain name (in other words, addresses@yourdomain.com are handled by Google). Your web host can then continue to serve web pages as usual.
There are many reasons for letting Google handle your e-mail:
- Spread your risk: If your website is having troubles, your e-mail service can often (but not always, depending on your setup) continue to function normally with the external provider.
- Use Google’s infrastructure: Why bog down your server when you can let Google do all the heavy e-mail lifting? Say goodbye to clogged e-mail queues.
- Storage space: With Google currently offering more than 7 gigabytes for each e-mail account, this is twice the amount of space per e-mail account (and by default Google Apps gives you 100 accounts) than what I use for all of my websites combined.
- Gmail features, but no Gmail interface lock-in: Gmail has some really great features such as powerful filtering rules and a good anti-spam blocker. Plus, if you’re like me and don’t actually like the Gmail user interface, you can let Gmail handle the initial mail processing but then forward your mail elsewhere (in my case, that’s to Yahoo! Mail). You can also configure external web and desktop clients to access your e-mail via the standard POP and IMAP protocols.
- Free yourself from other spammers on your web server: If Gmail users are using their accounts to spam, Google will theoretically deal with those users without affecting your service.
Setting up Google Apps for your domain
I’m not going to go through each step for managing your domain’s e-mail through Google Apps, because it’s actually quite straightforward after you sign up.
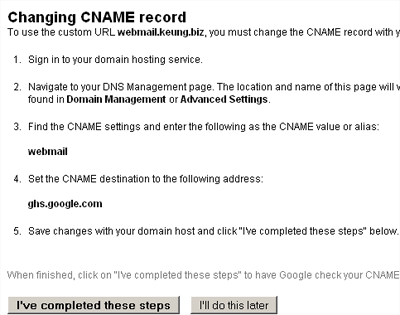
In order to have your domain name automatically point to Google as the handler of all things e-mail, you need to change the MX records through either your web host, your domain registrar, or your external DNS provider. There are some great Google instructions on this and there’s a good chance that they have instructions for your particular setup.
By default, your e-mail interface is then accessible via http://mail.google.com/a/yourdomain.com. However, with a bit of work you can also redirect something like http://webmail.yourdomain.com there.
As I mentioned earlier, Google Apps usually lets you have 100 user accounts under one domain for free. Under the free service, you can also: add e-mail aliases (like having pete@yourdomain.com forward to the desired peter@yourdomain.com address); have synced domains (like having all configured users @yourdomain.com also work in a mirrored way for @yourdomain.ca); set up e-mail lists; take advantage of the other Google Apps for your domain such as Google Docs and Google Calendar; and more.
The Premium package costs $50 per user and gets you extra business features such as support, more storage, SSL enforcement, a single sign-on API, and no ads.
Da Tag(s): google apps Da Categorie(s): Email
Design Inspiration
Comments Off on Design Inspiration
Da Tag(s): design ideas Da Categorie(s): Design
How to Find and Replace Text in MySQL Database using SQL
Comments Off on How to Find and Replace Text in MySQL Database using SQL
MySQL database has a handy and simple string function REPLACE() that allows table data with the matching string (from_string) to be replaced by new string (to_string). This is useful if there is need to search and replace a text string which affects many records or rows, such as change of company name, postcode, URL or spelling mistake.
The syntax of REPLACE is REPLACE(text_string, from_string, to_string)
MySQL reference describes REPLACE as function that returns the string text_string with all occurrences of the string from_string replaced by the string to_string, where matching is case-sensitive when searching for from_string. text_string can be retrieved from the a field in the database table too. Most SQL command can be REPLACE() function, especially SELECT and UPDATE manipulation statement.
For example:
update TABLE_NAME set FIELD_NAME = replace(FIELD_NAME, 'find this string', 'replace found string with this string');
update client_table set company_name = replace(company_name, 'Old Company', 'New Company')
The above statement will replace all instances of ‘Old Company’ to ‘New Company’ in the field of company_name of client_table table.
Another example:
SELECT REPLACE('www.mysql.com', 'w', 'Ww');
Above statement will return ‘WwWwWw.mysql.com’ as result.
JQuery Tools Library by Flowplayer
Comments Off on JQuery Tools Library by Flowplayer
jQuery Tools is a collection of the most important user interface components for the web. These are tabs and accordions, tooltips, overlays, exposing effects and scrollables. They can dramatically improve the usability and responsiveness of your site. They mainly focus on presenting information and visual appeal. After all, this is exactly what most websites desperately want: to present their content to the reader in an easy and visually pleasing manner.
Other JavaScript UI libraries focus on desktop-like features such as drag-and-drop, sliders, sortable tables or draggable windows. They are meant to build “rich internet applications” (RIAs) such as email clients, task managers, CRM software, image organizers or feed viewers. These kind of applications are very useful within a small group or when used in intranets; however, normal websites are very different in nature. Their purpose is to look good and present information. jQuery Tools are built exactly for that purpose.
It is recommended that you start designing your pages without using any JavaScript. There are many examples of highly functional, good looking and user friendly web sites that are not using JavaScript. The purpose of this library is to enhance an existing site with the great possibilities that modern JavaScript techniques has to offer. This is essentially the idea of “progressive enhancement” which is a common design pattern today. You should realize that highly professional sites don’t overuse JavaScript just for the fun of it. Scripting is only used when it truly makes the pages more readable and user friendly. This is where these tools comes in to play.
This library is not a framework with a steep learning curve, lots of preliminary work and strict coding rules. You are not tied to any predefined HTML or CSS structures. You can include the library on your pages and start using it immediately. You can freely design the look and feel of your site or you can use the desing we have on our demos as a template.
These tools can be easily combined. Think of scrollables that trigger overlays or overlays that contain scrollables together with tooltips or whatever combination you can imagine. The possibilities are endless. And if that is not enough, you can harness the enormous power of the jQuery library. Many times you see complex JavaScript components implemented that could be done with just a few lines of jQuery code. For many websites, this may be the only JavaScript library necessary.
http://flowplayer.org/tools/using.html
Tools include:
- tabs
- tooltip
- scrollable
- overlay
- expose
- flashembed
Da Tag(s): coding standards, jquery Da Categorie(s): Javascript
PHP Query String Help
Comments Off on PHP Query String Help
Query strings play important role in building web applications, especially if you want to make nice urls without question mark and many key, value pairs, actually it is not so easy to design application with nice urls however it is always worth doing so, because it not only looks very proffessional, such URLs are search engine friendly, which means that they will get indexed faster but also it happens that search engines have problems with indexing pages with more then 3 key=value pairs in query string.
However, one place where using nice URLs is not neccessary are all kinds of admin panels, there are usually only few admins and more over admin panel never gets indexed so it doesn’t make any sense to make those URLs search engine friendly.
Query string can be accessed thru global array $_SERVER, more specific $_SERVER[‘QUERY_STRING’] is the actual variable where query string is written, this variable contains all data that is inputed after question mark in the URL. For example if we have URL which looks like this:
http://someurl.com/page.php?a=1&b=2&c=3
Then echo $_SERVER[‘QUERY_STRING’] will display: a=1&b=2&c=3, such data is no use to us, we need to parse it, or get it thru global array $_GET, in our case we could write:
echo $_GET['a']; echo $_GET['b']; echo $_GET['c'];
which would output:
1 2 3
Two things i have to mention here:
– i do not recommend displaying variables passed by user withut checking if they contain potentially dangerous code.
– make sure you have register_globals set to off in your ini file. If you do not have access to ini file, you can change this setting in your .htaccess file (if you have htaccess files working on your server). To do this just add following line php_flag register_globals off.
Using $_GET array to access variables from query string is pretty simple, however we would want to transform our URL to make it look like this:
http://someurl.com/1/2/3
This is very search engine friendly approach, however like always there are no roses without thorns. First problem is that $_SERVER[‘QUERY_STRING’] variable is empty now, so $_GET array is empty as well.
But first thing first, we can’t just input this URL in web browser address bar, hit enter and wait for a page to load. Probably it would end with 404 Error. To avoid this we need to create .htaccess file in the same directory as page.php file. Then open .htaccess file and write in it:
RewriteEngine on RewriteRule .* page.php
Now all requests to directory which contains file page.php will be redirected to page.php file. Pretty simple and we can now use URL without question mark or any other unwanted signs i provided earlier (e.g. http://someurl.com/1/2/3).
So as i said earlier now our $_GET array is empty, but fortunately we can still check what the URL looks like by writing this code:
echo $_SERVER['REQUEST_URI']; // output /1/2/3
Well, maybe URL looks pretty search engine friendly however id does not provide a lot of info as it did earlier. Unfortunately solution to this problem is beyond the scope of this article and i will give you only few guidlines: first you need to parse URL wit explode() to get array, then it will be good to assign some keys to each of the variable, but you always need to remember who is who, do not change order of parameters in the URL.
I covered only two types passing arguments to application with query string, there are other solutions as well, but i think that this two are the most common used and are actually the best when it comes to PHP.
Da Tag(s): coding standards, php Da Categorie(s): Code